If a vehicle is overheating, the diagnostic process has become more complicated in modern cooling systems. Part of the reason is cooling systems have become more integrated with the engine management and emissions reduction systems. Old cooling systems reacted to heat generated by the engine. New systems anticipate and influence changes in coolant temperature.
To gain control over coolant temperature, OEMs have introduced several new cooling system components that can control the flow and temperature of the coolant. These include grille shutters, electronic thermostats, flow control valves and electric water pumps.
To diagnose an overheating or overcooling complaint, the most important thing is to understand what happens when a component fails and how the control system reacts.
Grille Shutters
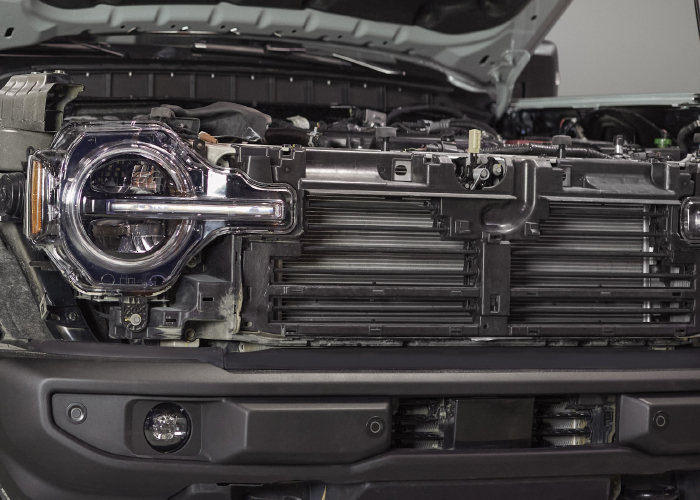
Ford, BMW and many other OEMs have been including active grille shutters on vehicles over the past decade. The system optimizes aerodynamics and coolant temperatures by using electronically controlled slats to control airflow through the grille, radiator and engine compartment.
If air is required to cool the engine, the vents are opened. If no airflow is needed, the vents are shut, contributing to significantly reduced aerodynamic drag. These systems keep the vanes closed as long as possible from a cold start.
The technology can reduce the amount of time required to get the coolant and oil up to temperature during a cold start. Depending on the ambient air temperature and vehicle speeds, the active shutters can reduce emissions and the time to reach closed-loop operation.
Mounted ahead of the radiator, active grille shutters have motorized horizontal vanes that can rotate to block airflow. The ECM can control the pitch of the vanes to control the air passing through the radiator. Ford has 15 settings, while other manufacturers use a percentage of opening requested.
The last thing the OEM wants to do is to have the shutter stuck closed. If the grille is stuck in the closed position, the engine will overheat. To prevent this from happening, the fail-safe position is typically fully open. When the car or truck is parked, the shutters will be in the fully open position. When the engine is started, the actuator will test the shutters’ full range of motion. If an issue is detected, the ECM puts the shutters in a fully open or neutral position and does not actuate them. The ECM will set a code and turn on the check engine light if a problem is detected.
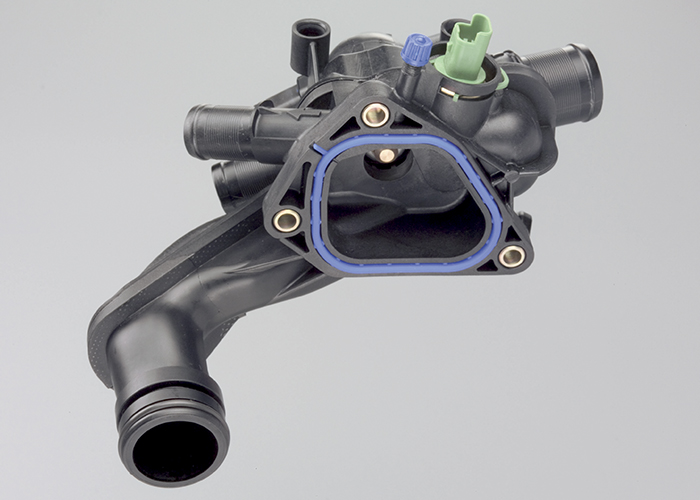
Electronic Thermostats
A conventional thermostat reacts to changes in the temperature of the coolant. It is a simple reaction where heat causes a capsule of wax to melt. When the wax melts, a spring can push the valve open and coolant flows. When the coolant drops in temperature, the wax solidifies, and the valve closes.
An electronic thermostat can preemptively control the temperature of the coolant by heating the wax capsule with an electric heating element controlled by the ECM. The system can liquify the wax and open the thermostat.
With a conventional thermostat, if the driver encounters a large hill, the cooling system reacts to the increased heat generated by the engine loads. The transferred heat has to pass through the cylinder head, block and the housing that holds the thermostat. By the time this happens, the engine could be experiencing detonation, pre-ignition and increased NOX emissions.
With an electronic thermostat, the ECM will command the thermostat open when load is put on the engine. Factors like ambient temperature, engine RPM and ignition time can influence the position of the thermostat. These inputs can be configured into a “map” that can optimize engine performance.
The failure mode for an electric thermostat is if the heater fails, it will work as a conventional thermostat. The ECM might detect increased or decreased resistance in the heater circuit and set a code. But, other codes can be set if the ECM does not see temperature changes when the thermostat is opened or closed.
Flow Control Valves
Even the latest electronic thermostats have their limitations. Many new engine designs use a thermal or flow control valve. These valves direct the flow of the coolant, instead of blocking coolant flow like a conventional thermostat. The valve can direct coolant to the engine as well as the turbocharger, heater core and oil cooler. By controlling coolant flow, the time to reach closed-loop operation is reduced.
Flow control valves have a stepper motor similar to those found on a throttle-by-wire actuator. Inside are position switches that monitor the location of the valves. The position of the valves can be set depending on the engine load, coolant temperatures and other parameters like the temperature of the heater core.
The failure mode for a flow control valve is similar to grille shutters. When a problem is detected, it will go into a neutral position where the flow is directed to vital components like the engine block, cylinder head and turbocharger. The component will set codes, and the driver may notice it takes longer to warm up the engine, as well as a reduction in fuel economy.
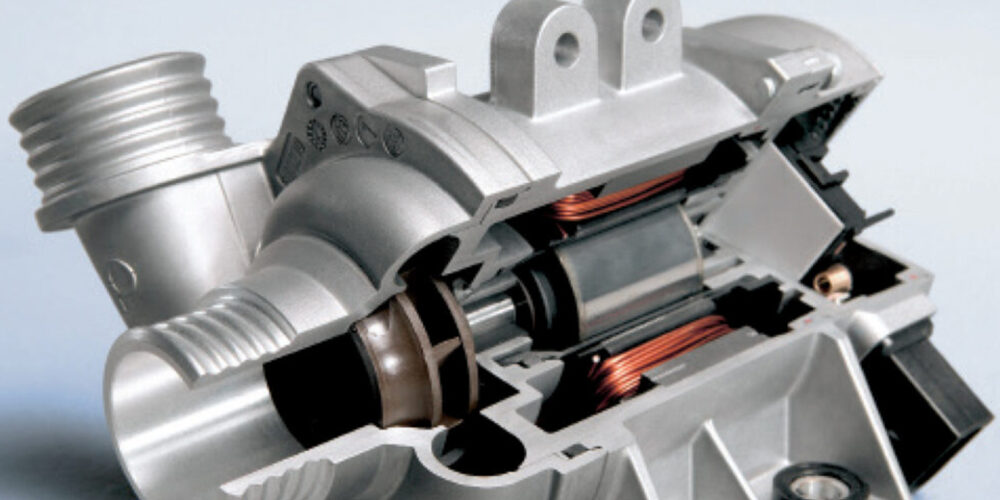
Electric Water Pumps
A mechanical water pump can be turned by a timing chain, timing belt or drive belt and is limited by the speed of the engine. These mechanical pumps might not move enough coolant at idle, or it could be cavitating at higher rpm. Also, the pump can use 3-5 hp from the engine. The solution is to use an electric motor to turn the water pump.
The most infamous application is the BMW N54, but other domestic, European and Asian manufacturers are using these styles of water pumps. These types of pumps constantly vary the speed of the pump to control the temperature of the engine. Temperature sensors on the engine, radiator and HVAC system will check the effectiveness of the pump to move the coolant and transfer heat.
If the pump can’t control the temperature, it will set a code for the pump that may describe the problem as a deviation in speed. The system might try to increase the speed of the pump to preserve the engine. But, if the pump is no longer turning, the engine will overheat.
The other type of electric water pump is an auxiliary coolant pump. These pumps can operate when the key is off or on. The first application was to keep the coolant moving through the heater core on diesel-powered vehicles so the driver would not freeze while the vehicle was idling. These pumps are also used to cool a turbocharger after the engine has shut down.
A failed auxiliary pump will almost never cause the vehicle to overheat. If the auxiliary coolant pump is inoperative, the customer might notice reduced heater performance at low speeds and at idle. If the pump is used to cool the turbocharger, the failed pump can cause the turbocharger to fail prematurely.
The basics still apply to modern cooling systems. If the system can’t maintain pressure, the system will overheat. Also, the quality of the coolant will determine the longevity of the components. The only real change is that you will need a scan to verify the operation of these new components.