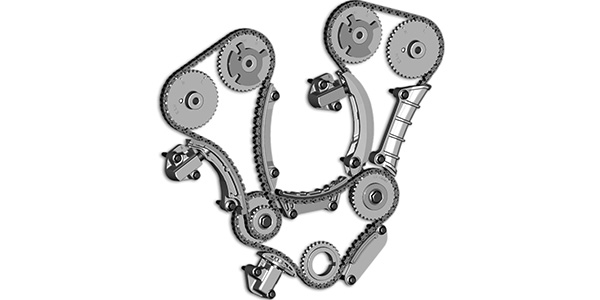
What does a timing chain do?
A timing chain synchronizes the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft(s) ensuring proper timing and allows the engine’s valves to open and close during each cylinder’s firing. The chain is located inside of the engine and needs to be lubricated by the oil in the engine, making oil maintenance important as well. Every time you use the engine, the timing chain is in use.
When does a timing chain need to be replaced?
The timing chain normally needs to be replaced between 80,000 and 120,000 miles unless there is a specific problem. Issues with the chain are common in higher mileage vehicles. If driving an older vehicle, or one with close to 100,000 miles, it is recommended to look for symptoms of the timing chain going bad or failing.
Since the timing chain can go bad and will need to be replaced, it is important to be able to recognize the symptoms and have it repaired before it fails completely.
Signs a timing chain needs to be replaced include:
- Later model VVT applications will generate engine codes and check engine lights prior to engine rattle
- Older, pre-VVT applications will generate engine rattle
What causes timing chain noise?
Timing chain noise is commonly most noticeable during cold startup of the vehicle when oil pressure and oil flow is at its lowest. Excess slack in the timing chain can cause a rattling sound or even a clanking sound if the slack is severe enough to cause the chain to contact the timing chain cover. If the engine is equipped with a hydraulic timing chain tensioner, the noise may disappear or lessen as the engine oil warms up and the tensioner removes some of the slack. If the timing chain wear is great enough so the tensioner can no longer compensate for the slack, the noise may continue even after warming up.
What signals timing chain damage?
In many cases, timing chains stretch due to improper owner maintenance. Going too long between oil changes and using the wrong type or viscosity rated motor oil causes the timing chain pins and plates to wear, resulting in timing chain stretch. Timing chain pin and plate wear is accelerated by contaminates in the oil, that is the reason frequent oil changes are required. It is not that the old oil doesn’t lubricate, particulates that get trapped in the oil that work between the pin/plates will create accelerated wear. In addition to oil change neglect and improper oil usage, using the wrong or low-quality oil filter can also cause accelerated timing chain wear.
Should I also replace sprockets?
Yes, Cloyes recommends that all components of the timing system be replaced at the same time. Using a worn sprocket may result in the chain not meshing with the worn sprocket, which could result in poor engine performance. Cloyes offers a wide range of complete timing chain kits for majority of vehicles on the road today.
What causes a timing chain to break or wear?
Over time, the timing chain stretches due to internal component wear. The chain tensioner or the guides that are connected to the timing chain may wear out as well, causing the timing chain to fail completely. If the chain fails, the vehicle will not run at all.
How important is oil quality?
Using the wrong oil is a common symptom that causes a vehicle’s timing chain to wear even quicker. Often, modern vehicles will only be able to use synthetic oil because they must meet certain specifications to ensure the oil flows quickly, and with the proper pressure. The wrong oil can cause extra load on the chain and the engine will not be properly lubricated.
Each vehicle manufacturer specifies a minimum API oil service rating, a recommended viscosity, and often a specific oil. Improper oil viscosity can also have a serious impact on timing chain tensioner operation, variable valve timing solenoids and actuators, and direct injection fuel pump wear. In fact, using a motor oil viscosity other than the factory recommended oil can result in a check engine light and engine damage.
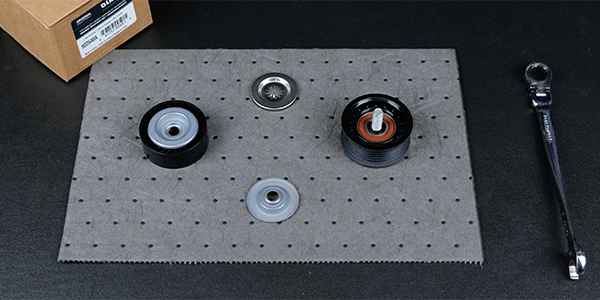
Should I replace the accessory drive belt when replacing a timing chain?
The timing chain is located inside the engine which requires several steps to get to the timing drive, making timing chain and timing drive component inspection and replacement difficult. When replacing the timing chain, it’s important that the accessory belt, tensioner, idler pulleys, and water pump are inspected as these components wear at a similar rate. These components are inexpensive when compared to labor costs.
This article was sponsored by Cloyes Gear & Products. For more information, visit https://www.cloyes.com/.